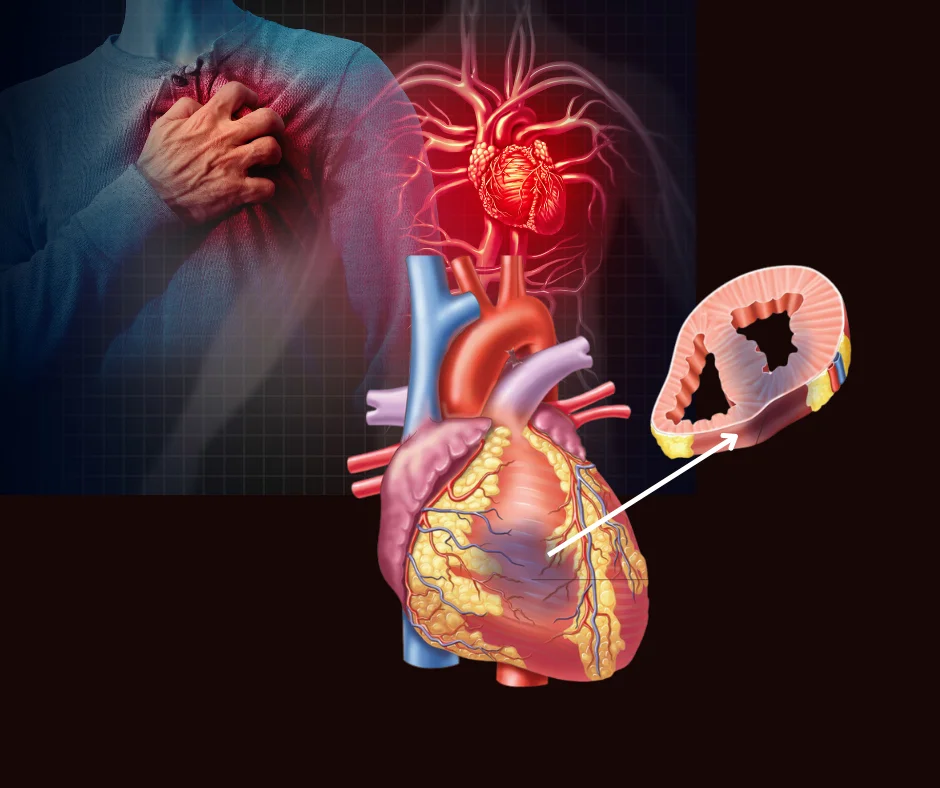
Heart Attack | The Most Common Cardiac Cause Of Death
Definition Heart attack or Myocardial infarction (MI) is defined as myocardial necrosis which occurs as a result of a critical imbalance between coronary blood flow and myocardial demand due to…
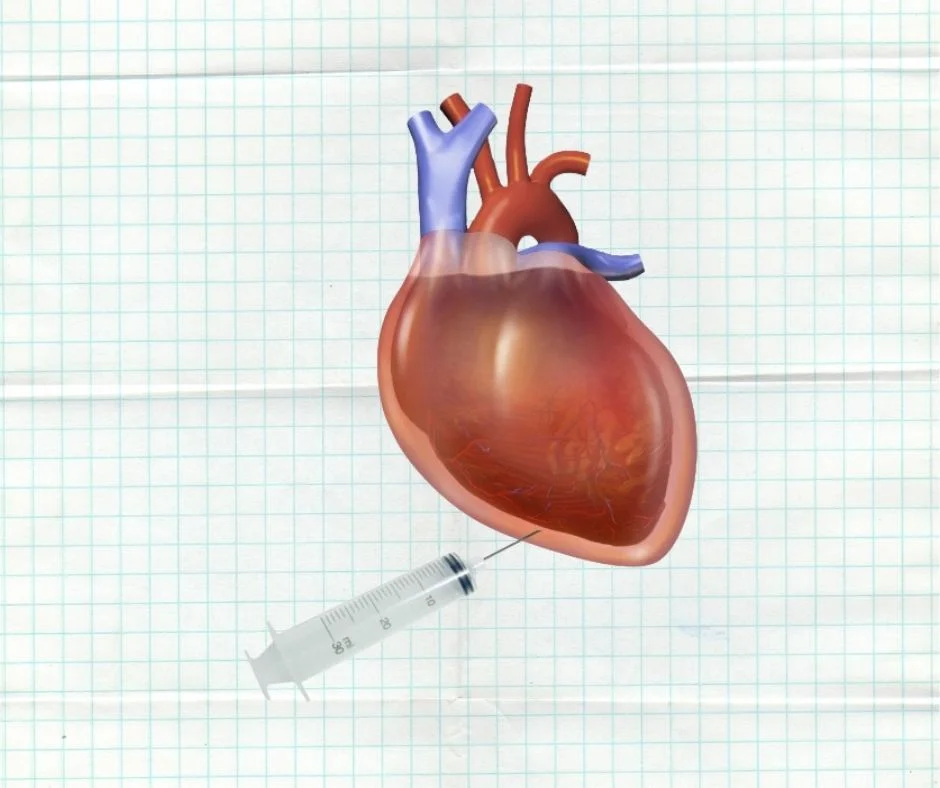
Pericardiocentesis
Definition It is the aspiration of pericardial fluid. Done under ultrasonographic or echocardiographic guidance. Aspiration needle is introduced through the left costoxiphoid junction, directed upwards, backward, and towards the left…
What is Monkey Pox?
History of Monkey Pox Virus Smallpox became extinct in 1990. The monkeypox is a member of that smallpox family – orthopoxvirus. The virus was first detected in monkeys in 1958,…
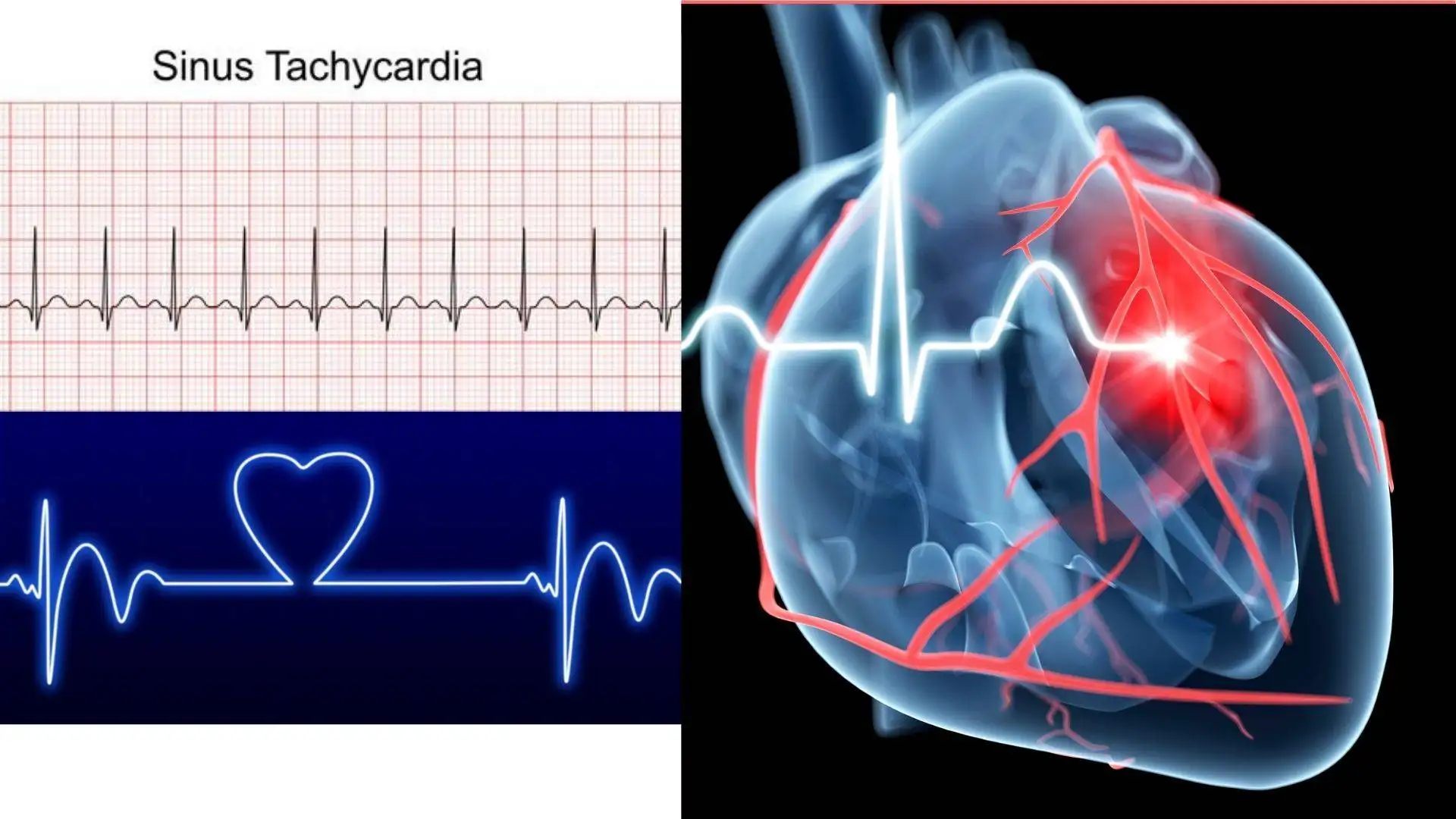
Sinus Tachycardia
Definition When the heart rate is greater than 100/min in sinus ( rhythm. Causes 1. Physiological—anxiety, emotion, exercise, pain, pregnancy. 2. Pathological— –– Anaemia. –– Fever. –– Thyrotoxicosis. –– Shock…
Treatment Goals for Adults with Diabetes
HbA1c : < 7.0% Preprandial capillary plasma glucose: 4.4 – 7.2 mmol/L (80 -130 mg/dL) Postprandial capillary plasma glucose: <10 mmol/L (<180 mg/dL) Blood Pressure: <140/90 mmHg Ref: Harrison’s Principles…
Causes of Bronchiectasis
What are the causes of Bronchiectasis? 1. Congenital or hereditary— – Cystic fibrosis. – Kartagener’s syndrome (triad of bronchiectasis, dextrocardia and sinusitis or frontal sinus agenesis). – Primary ciliary dyskinesia…
Ventricular Tachycardia
Definition of Ventricular Tachycardia Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is defined as three or more consectutive ectopic beats, heart rate usually 140–220 beats/minute with regular rhythm. Causes of Ventricular Tachycardia • Acute…
Ventricular Fibrillation
Definition of Ventricular fibrillation Ventricular fibrillation (VF) is a type of ventricular arrhythmia characterised by rapid, irregular, ineffective and uncoordinated ventricular activation with no mechanical effect. There is chaotic electrical…
Marfan’s Syndrome
What is Marfan’s Syndrome Definition It is a connective tissue disorder inherited as autosomal dominant trait due to mutation in the fibrillin-1 gene, a component of extracellular matrix. The fibrillin…
Pacemaker
What is Pacemaker Pacemaker is an artificial device used to electrically stimulate the heart. It is composed of two parts: • Battery-powered generator. • Wire electrode—which is attached to the…
Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB)
ECG Criteria of LBBB • RSR´- in V5 and V6, also in L1 and aVL (M pattern). • QRS wide, >0.12 second (3 small squares). Causes of LBBB • Severe…
Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)
What is RBBB The full terms of RBBB is Right Bundle Branch Block ECG Criteria • RSR—in V1 and V2 (M pattern). • QRS—wide, >0.12 second (3 small squares). Causes…
Complete Heart Block
What is Complete Heart Block No impulse from atria transmitted to the ventricles. So, ventricles generate their own rhythm. Causes of Complete Heart Block (CHB) 1. Acute CHB—Acute MI (commonly…