Second Degree AV Block
What is Second Degree AV Block Types It is of 3 types: • Mobitz type I (Wenckebach’s phenomenon). • Mobitz type II. • 2 : 1 or 3 : 1…
First Degree AV Block
What is First Degree AV Block It is the prolongation of PR >0.22 sec. Every atrial depolarisation is followed by conduction to the ventricles, but with delay. Causes of First…
SA Block (Sinoatrial Block)
What is SA Block Failure to inititate an impulse from SA node. Causes of SA Block • Degenerative changes in elderly. • Ischaemic heart disease (involving SA node). • Drugs…
Heart Block
Definition of Heart Block It is defined as defect in either initiation or conduction of cardiac impulse. Sites of Heart Block • SA node. • AV node. • Bundle of…
Cardiac Arrest
What is Cardiac Arrest It is defined as sudden loss of cardiac function, when the heart abruptly stops beating. Causes of Cardiac Arrest 1. Ventricular fibrillation (commonest cause). 2. Ventricular…
Pulmonary Hypertension
What is Pulmonary Hypertension It is defined as mean pulmonary arterial pressure > 25 mm Hg at rest and > 30 mm Hg during exercise. Causes of Pulmonary Hypertension 1.…
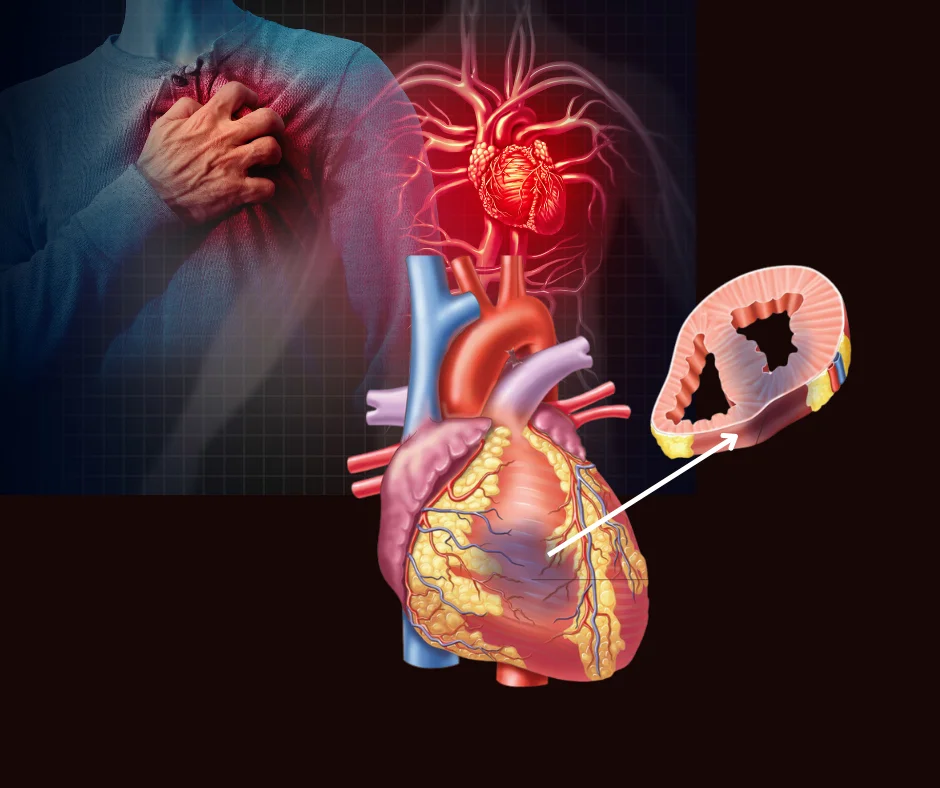
Heart Attack | The Most Common Cardiac Cause Of Death
Definition Heart attack or Myocardial infarction (MI) is defined as myocardial necrosis which occurs as a result of a critical imbalance between coronary blood flow and myocardial demand due to…
Angina Pectoris
Definition It is defined as paroxysmal precordial pain of short duration due to transient (temporary) myocardial ischaemia. Clinical Features Symptoms Main symptom is pain which has the following characters— •…
Ischaemic Heart Disease
Ischaemic heart disease (IHD) results from reduced coronary blood flow to the myocardium, when there is an imbalance between the supply of oxygen and myocardial demand. IHD includes angina pectoris…
Cardiac Tamponade
Definition It is a state of compression of the heart in rapidly developing pericardial effusion. It interferes with the diastolic filling of the heart and the patient develops features of…